Research Abstract
発火タイミング依存可塑性によって文字画像の時系列を記憶する7個の人工ニューロン
Seven neurons memorizing sequences of alphabetical images via spike-timing dependent plasticity
2015年9月16日 Scientific Reports 5 : 14149 doi: 10.1038/srep14149
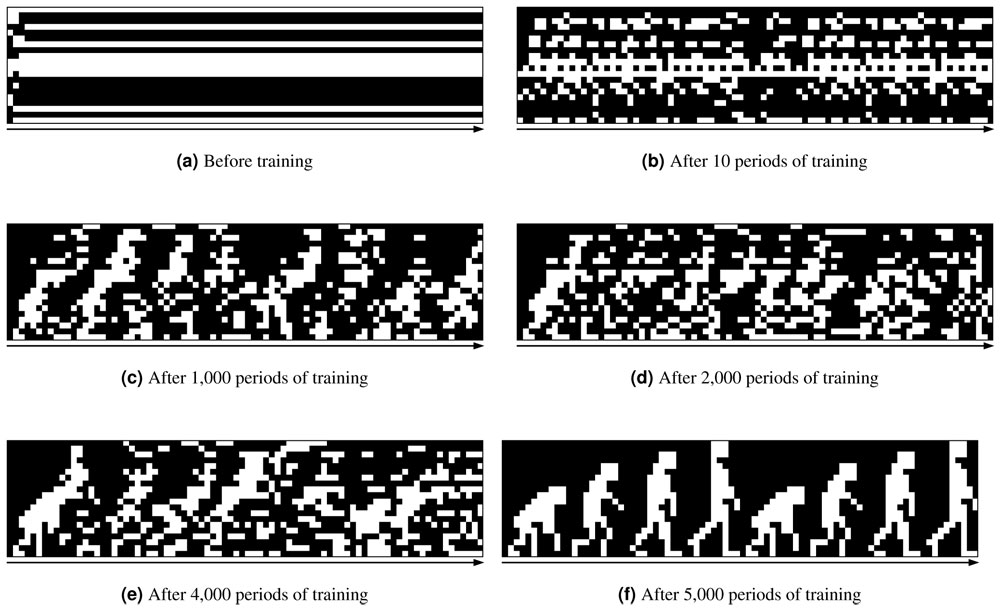
ボルツマンマシンのような人工神経ネットワークは、静的なパターンを記憶し、関連する手がかりが与えられるとそれを想起するよう、ヘッブ則によって訓練することができる。しかし、そうしたネットワークは、時間変化するパターンに対しては、生物のようにうまく学習することができない。今回、生物の神経ネットワークで観測されている、発火タイミング依存可塑性(STDP)の性質を取り込んだ規則で学習する、動的ボルツマンマシン(DyBM)を考案した。7個の人工ニューロンから成るDyBMに対して、「SCIENCE」の文字画像の時系列とその逆順の時系列を記憶するよう訓練したあと、どちらかの時系列の一部を手がかりとして提示すると、対応する時系列の全体を想起させることができた。DyBMにおけるSTDPは、ボルツマンマシンにおけるヘッブ則に相当する学習規則である。
Takayuki Osogami & Makoto Otsuka
Corresponding Author
An artificial neural network, such as a Boltzmann machine, can be trained with the Hebb rule so that it stores static patterns and retrieves a particular pattern when an associated cue is presented to it. Such a network, however, cannot effectively deal with dynamic patterns in the manner of living creatures. Here, we design a dynamic Boltzmann machine (DyBM) and a learning rule that has some of the properties of spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP), which has been postulated for biological neural networks. We train a DyBM consisting of only seven neurons in a way that it memorizes the sequence of the bitmap patterns in an alphabetical image “SCIENCE” and its reverse sequence and retrieves either sequence when a partial sequence is presented as a cue. The DyBM is to STDP as the Boltzmann machine is to the Hebb rule.

